Introduction
Solar panels have become a ubiquitous feature on rooftops and in solar farms around the world. They are a clean and sustainable source of electricity, but not all solar panels are created equal. The efficiency of a solar panel is a critical factor that determines its ability to convert sunlight into electricity. In this blog post, we will explore the various factors that affect the efficiency of solar panels and how optimizing these factors can lead to better solar energy production.
Understanding Solar Panel Efficiency
Solar panel efficiency refers to the percentage of sunlight that a solar panel can convert into electricity. In other words, it measures how effectively a solar panel can harness the energy from the sun and turn it into usable electrical power. Efficiency is typically expressed as a percentage and can vary widely depending on several factors.
Factors Affecting Solar Panel Efficiency
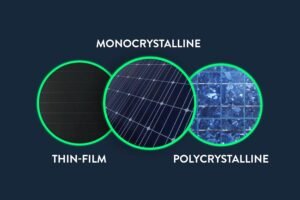
- Solar Cell Type: Different types of solar cells have varying levels of efficiency. The most common types are monocrystalline, polycrystalline, and thin-film solar cells. Monocrystalline cells tend to be the most efficient, followed by polycrystalline and thin-film cells.
- Quality of Materials: The quality of the materials used in the manufacturing of solar panels can significantly impact their efficiency. High-quality materials, such as the semiconductor material and the anti-reflective coating, can enhance the panel’s ability to capture and convert sunlight.
- Temperature: Solar panels are sensitive to temperature changes. Higher temperatures can reduce efficiency. Solar panels are often rated at a standard test condition (STC), which assumes a specific temperature. In real-world conditions, efficiency can drop as temperatures rise.
- Angle and Orientation: The angle and orientation of solar panels affect how much sunlight they can capture. Panels should be tilted and oriented to maximize exposure to sunlight throughout the day and across the seasons.
- Shading: Even partial shading of a solar panel can significantly reduce its efficiency. Obstructions like trees, buildings, or debris should be avoided to ensure maximum sunlight exposure.
- Dirt and Dust: Accumulated dirt, dust, or debris on the surface of the solar panels can block sunlight and reduce efficiency. Regular cleaning and maintenance are essential to maintain optimal performance.
- Inverter Efficiency: Inverters are used to convert the direct current (DC) generated by solar panels into alternating current (AC) for use in homes and businesses. The efficiency of the inverter plays a role in the overall system efficiency.
- Aging and Degradation: Over time, solar panels can degrade in performance. Manufacturers typically provide a warranty specifying the expected degradation rate over the panel’s lifetime.
- Reflection and Glare: Reflective surfaces near solar panels can cause glare, which may reduce efficiency and be a nuisance to nearby residents.
- Tilt and Tracking Systems: Some advanced solar installations incorporate tracking systems that follow the sun’s path throughout the day. These systems can significantly boost efficiency by keeping the panels aligned with the sun.
Maximizing Solar Panel Efficiency
To maximize the efficiency of your solar panel system, consider the following tips:
- Choose high-quality solar panels with reputable manufacturers.
- Ensure proper installation with the right angle and orientation.
- Keep the panels clean and free of obstructions.
- Invest in efficient inverters.
- Monitor your system’s performance regularly.
- Consider technologies like solar tracking systems if feasible.
Conclusion
Solar panel efficiency is a critical factor in determining the effectiveness of a solar energy system. Understanding the factors that affect efficiency and taking steps to optimize them can result in increased energy production and a better return on your investment. As solar technology continues to advance, we can expect even more efficient and cost-effective solar panels in the future, further enhancing the appeal of renewable energy sources.

