Introduction
Solar energy is becoming an increasingly popular choice for powering homes and businesses around the world. Solar panels, which convert sunlight into electricity, are at the heart of this renewable energy revolution. When it comes to selecting solar panels for your installation, two main types dominate the market: monocrystalline and polycrystalline panels. In this technical blog, we’ll dive deep into the differences between these two technologies to help you make an informed decision for your solar power needs.
Understanding the Basics
Before we get into the nitty-gritty details, let’s start with a basic understanding of monocrystalline and polycrystalline solar panels.
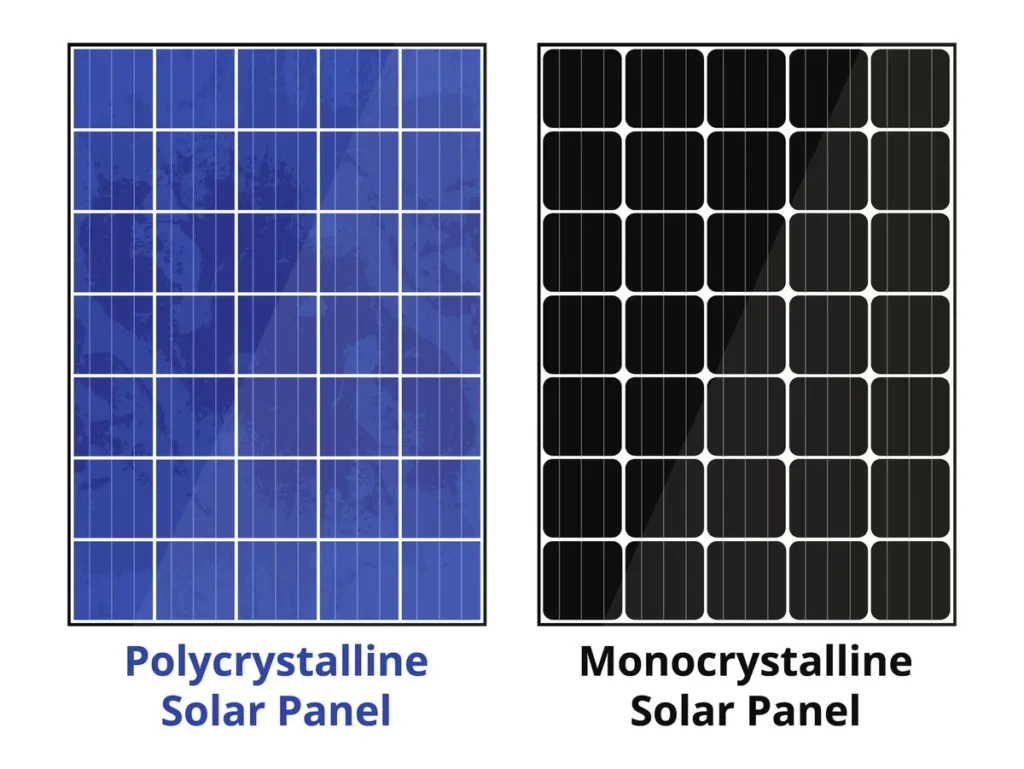
Monocrystalline Solar Panels:
- Made from a single crystal structure.
- High efficiency and space-efficient.
- Typically, black in colour.
- More expensive to produce but often more efficient.
Polycrystalline Solar Panels:
- Made from multiple crystal structures.
- Slightly less efficient and space-consuming than monocrystalline panels.
- Typically, blue in colour.
- More cost-effective to produce.
Now, let’s delve deeper into these differences to help you make an informed decision.
Efficiency and Space Efficiency
One of the most significant factors to consider when choosing between monocrystalline and polycrystalline panels is efficiency. Efficiency in this context refers to how well a solar panel converts sunlight into electricity.
Monocrystalline Panels:
- High efficiency: Typically, monocrystalline panels have a higher efficiency rate (around 15-22%) compared to polycrystalline panels.
- Space-efficient: They require less space to generate the same amount of electricity, making them ideal for installations with limited roof space.
Polycrystalline Panels:
- Slightly lower efficiency: Polycrystalline panels usually have an efficiency rate of 13-16%, which is slightly lower than monocrystalline panels.
- Space-consuming: Due to their lower efficiency, they require more space to generate the same amount of power, which may be a consideration if you have limited roof area.
Cost
Cost is another crucial factor in the choice between monocrystalline and polycrystalline solar panels.
Monocrystalline Panels:
- More expensive: Monocrystalline panels are generally more costly to manufacture due to their single crystal structure and higher efficiency.
- Lower cost per watt: However, when you consider the higher efficiency, they often have a lower cost per watt of electricity generated.
Polycrystalline Panels:
- Cost-effective: Polycrystalline panels are less expensive to produce because they use multiple crystal structures. • Higher cost per watt: Despite their lower upfront cost, they may have a slightly higher cost per watt due to their lower efficiency.
Appearance
While appearance might not be the primary consideration, it can be a factor for some homeowners.
Monocrystalline Panels:
- Typically black or dark blue.
- Sleek and uniform appearance, often considered more aesthetically pleasing.
Polycrystalline Panels:
- Typically blue.
- Less uniform and may have a speckled appearance due to the multiple crystal structures.
Temperature Tolerance
The temperature tolerance of solar panels is an important consideration, especially in regions with extreme weather conditions.
Monocrystalline Panels:
- Generally, have better temperature tolerance, which means they perform better in high-temperature environments.
Polycrystalline Panels:
- May have slightly lower temperature tolerance, which can result in reduced efficiency in hot climates.
Conclusion
In summary, the choice between monocrystalline and polycrystalline solar panels depends on your specific needs and priorities. Monocrystalline panels offer higher efficiency and space efficiency but come at a higher upfront cost. Polycrystalline panels are more cost-effective but slightly less efficient.
Consider factors such as available roof space, budget, aesthetic preferences, and local climate conditions when making your decision. Ultimately, both types of panels can harness the power of the sun to generate clean and renewable energy for your home or business. Your choice should align with your goals for solar energy production and your budget constraints.