Blog Details
Building Information Modeling (BIM) and 3D Modeling with Revit Architecture: A Case Study
Introduction to BIM
Building Information Modeling (BIM) is a comprehensive process that integrates the collection of various types of data, the design phase, and the execution of construction tasks. Advanced software like Revit is commonly used to create detailed 3D models of buildings, enhancing collaboration and improving the efficiency of architectural projects.
BIM Stages
1. Conceptualization and Design
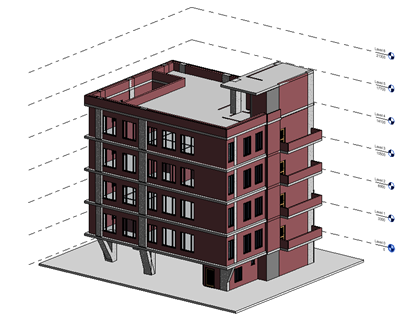
During the initial stage, architects and engineers use BIM software to develop virtual models of the building. These models help stakeholders visualize the project, assess its performance, and make informed design decisions.
2. Construction Planning and Coordination
BIM models facilitate effective planning and coordination during construction. They allow teams to schedule activities, organize workflows, and identify potential clashes using tools for clash detection. By addressing issues early, BIM minimizes delays and reduces rework.
3. Construction Execution
In the construction phase, BIM supports project execution through accurate material estimates, detailed schedules, and enhanced team communication. Contractors can track progress, manage resources, and oversee subcontractors efficiently with BIM’s integrated tools.
4. Facility Management and Operation
Once the project is complete, BIM models serve as valuable resources for facility managers. They provide detailed information about building components, maintenance schedules, and energy usage, enabling proactive maintenance and efficient building operations.
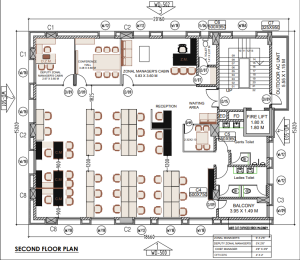
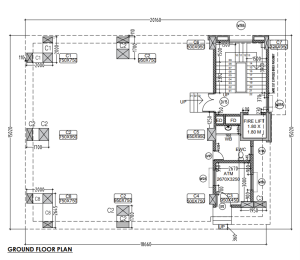
3D Modeling of a Commercial Building: Process and Challenges
Process
Challenges
-
- Converting 2D Plans to 3D Models: The transition from 2D plans to a comprehensive 3D model posed a significant challenge, leading to delays in project progress.
-
- Construction Knowledge Gaps: A lack of familiarity with construction-related standards, such as standard door and window head heights, created additional difficulties.
- Custom Component Design: Developing custom-designed components, such as furniture (chairs, tables, etc.), required the creation of families within Revit, which proved to be a time-intensive process.
Conclusion
Recent Posts



Categories
Have a project in mind?
Schedule a Call
Just One Call Away – Let’s Talk Solutions!
Call Us +91 7338189979